
Altera Corporation, based in San Jose, California, was a programmable logic device (PLD) manufacturer. Intel bought it in 2015 after it was formed in 1983.
Catalog
Ⅴ Altera(Intel) Alternate Names
Ⅰ Altera Company Profile
Introduction
Altera Corporation, based in San Jose, California, was a programmable logic device (PLD) manufacturer. Intel bought it in 2015 after it was formed in 1983.
The Stratix, Arria, and Cyclone series system on a chip FPGAs, the MAX series complex programmable logic device and non-volatile FPGAs. Intel Quartus Prime design software and Enpirion PowerSoC DC-DC power solutions were Altera's core product lines.
With $500,000 in startup money, semiconductor veterans Rodney Smith, Robert Hartmann, James Sansbury, and Paul Newhagen formed the company in 1983. Altera Corporation's name was a play on the word "alterable," which referred to the type of chips it produced. The company forged long-term design cooperation with Intel in 1984, and in 1988, it went public through an initial public offering. Altera paid $50 million for Intel's PLD business in 1994.
Intel Altera/Altera Intel: Intel purchased the company on December 28, 2015.
Ⅱ Altera Products
1. FPGAs
What is Altera FPGA?

The Stratix , Arria, and Cyclone series system on a chip FPGAs, the MAX series complex programmable logic device and non-volatile FPGAs. Intel Quartus Prime design software and Enpirion PowerSoC DC-DC power solutions were Altera's core product lines.
With up to 1.1 million logic elements, integrated transceivers up to 28 Gbit/s, up to 1.6 Tbit/s of serial switching capability, up to 1,840 GMACs of signal-processing performance, and up to 7 x72 DDR3 memory interfaces at 800 MHz, the Stratix series FPGA Altera was the company's largest and highest bandwidth devices.
Northwest Logic was bought by the firm in September 2000 in order to expand its design services for the delivery of comprehensive system-on-chip solutions.
Altera released the SDK for OpenCL in May 2013, allowing software developers to utilize the high-performance capabilities of programmable logic devices.
2. System on a chip FPGAs
The company began producing systems on chip FPGA devices in December 2012, using a fully depleted silicon on insulator (FDSOI) chip fabrication technique. On a single device, these devices combined FPGAs with full hard processor systems based on the ARM architecture.
3. What is Altera Quartus/Quartus Altera used for?
The Altera Quartus II design software provides a complete, multiplatform design environment that easily adapts to your specific design needs. It is a comprehensive environment for system-on-a-programmable-chip (SOPC) design. The Altera Quartus II software includes solutions for all phases of FPGA and CPLD design.
4. PowerSoC

In May 2013, Altera paid $140 million in cash for embedded power chipmaker Enpirion, which provided Altera with power system on a chip DC-DC converters that allowed for higher power densities and lower noise performance than their discrete counterparts. Enpirion DC-DC converters were simulated, measured, validated, and production qualified at delivery, unlike converters constructed from discrete components.
5. Application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs)
Altera provided a publicly available ASIC design pipeline based on HardCopy ASICs that converted a finished FPGA design to a non-modifiable form. This design cycle lowered design security concerns as well as production costs for bigger volumes. Design engineers may use Stratix series FPGAs to prototype their designs before moving them to HardCopy ASICs when they were ready for volume production.
Hardware/software co-design and co-verification were made possible because to the unique design flow. The flow was tested and found to be 9 to 12 months faster than standard-cell solutions in bringing systems to market. For both FPGA and ASIC implementations, design engineers were able to use a single RTL, set of intellectual property (IP) cores, and Quartus II design tools. The test insertion was handled by Altera's HardCopy Design Center.
The Nios II FPGA soft processor core from Altera became available for standard cell ASIC designs in 2007.
6. Semiconductor intellectual property cores
Altera and its partners offered a variety of semiconductor intellectual property cores that design engineers could use as building blocks to accomplish certain operations in their system designs. IP cores eliminate some of the time-consuming tasks of constructing each block from scratch in a design. Altera purchased Designpro, a producer of IP cores, in 2000.
Soft processor cores for the Nios II embedded CPU, the Freescale ColdFire v1 core (free for Cyclone III FPGA ), and the ARM Cortex-M1 processor, as well as a hard IP processor core for the ARM Cortex-A9 processor, were available from Altera.
7. Design software
A shared design environment, Quartus II design software, supported all of Altera's devices. A subscription-based edition and a free Web-based edition of Quartus II software were both available. It contained productivity-boosting tools.
8. What is ModelSim-Altera?
ModelSim is a multi-language environment by Mentor Graphics, for simulation of hardware description languages such as VHDL, Verilog and SystemC, and includes a built-in C debugger. ModelSim can be used independently, or in conjunction with Intel Quartus Prime, PSIM, Xilinx ISE or Xilinx Vivado.
9. What is Altera USB Blaster?

Altera USB-Blaster? Download Cable interfaces a USB port on a host computer to an Altera FPGA mounted on a printed circuit board. ... You can use the USB-Blaster cable to iteratively download configuration data to a system during prototyping or to program data into the system during production.
10. What is Altera Cyclone IV?

Altera / Intel? Cyclone? IV FPGAs extend the Cyclone? FPGA series leadership in providing the market's lowest cost, lowest power FPGAs, now with a transceiver variant. Cyclone? IV GX devices offer an on-chip transceiver with an I/Os speed up to 3.125Gbps.
11. What is Altera MAX 10?
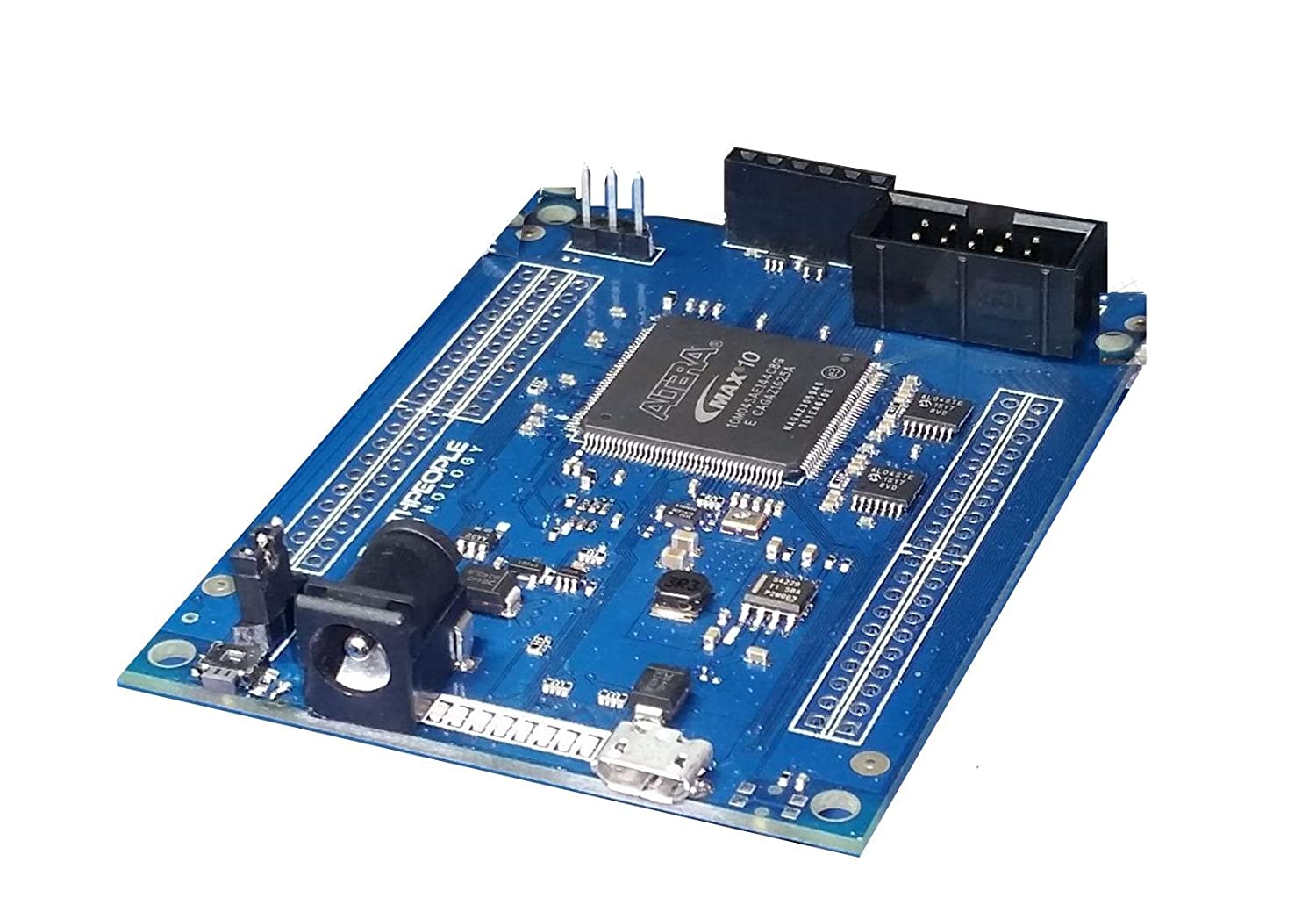
The MAX10 FPGA is a great chip to learn FPGA programming with. The MAX10 includes the configuration flash, 12 bit ADC, 20KByte of SRAM and low voltage regulators on chip.
Ⅲ Altera Technology
1. 40-nm technology
Altera released the Stratix IV FPGAs and HardCopy IV ASICs, the first 40-nm programmable logic devices, in May 2008. Optional integrated transceivers were provided for both devices.
Stratix IV GT FPGAs with 11.3 Gbit/s transceivers for 40G/100G applications and Arria II GX FPGAs with 3.75 Gbit/s transceivers for power- and cost-sensitive applications were released in February 2009.
Altera's devices were made with 193-nm immersion lithography and extreme low-k dielectrics and strained silicon, among other technologies.
2. 28-nm technology
The Stratix V FPGA (to Xilinx's Kintex-7 FPGA) was announced in April 2010 as the FPGA industry's second 28-nm device, having transceivers at speeds up to 28 Gbit/s. More than 1 million logic elements, up to 53 Mb of embedded memory, up to 7 x72 DDR3 DIMMs @ 800 MHz, 1.6 Gbit/s LVDS performance, and up to 3,680 variable-precision DSP blocks are available in this device family.
Altera began selling 28-nm Stratix V GT devices with 28-gigabits-per-second transceivers in August 2011.
Embedded HardCopy blocks protect standard or logic-intensive applications, improving integration and giving double the density without sacrificing cost or power. Altera created a user-friendly mechanism for partial reconfiguration, allowing for quick and easy changes to essential functionality. When designs are ready for volume production, there is a path to HardCopy V ASICs. Altera's 28 nm FPGAs were designed to cut power consumption to 200 mW per channel. In 2004, the company began working on HardCopy Structured ASICs alongside Synopsys .
The business announced the deployment of its first 28 nm Cyclone V SoC devices in December 2012, which featured a dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 processing system with FPGA logic on a single chip. Wireless communications, industrial, video surveillance, automotive, and medical device industries were all targets for these SoCs . Users were able to construct unique field-programmable SoC variants for power, board space, performance, and cost optimization using these SoCs devices.
3. 14-nm technology
Altera announced a partnership with Intel in February 2013 to use Intel's foundry services to build its 14-nm node for future FPGA manufacturing, based on Intel's 14 nm tri-gate transistor technology, replacing Altera's existing arrangement with TSMC.
STRATIX 10, based on Intel's 14 nm Tri-Gate technology, was launched in October 2016, over a year after Intel's integration with Altera.
Ⅳ Acquisition by Intel
In December 2015, Intel acquired Altera for $16.7 billion in cash.
Ⅴ Altera(Intel) Alternate Names
Altera(Intel) has several brands around the world that distributors may use as alternate names. Intel may also be known as the following names:
| • INT • INTEL CORP • CORTINA • DIGITAL • INTE | • ITL • INTL • INTEL CORPORATION • REI • INL | • ISP • TNTEL • NITEL • Intel / Altera • Intel Semiconductor Ltd | • INTEL CORPORATI • INT'L REC • INTEL MIL EOL • Intel Celeron • INTEL SEMICONDUCTOR | • INTEL XEON • INTEL COR • Intel (CPU) • INTEL (VA) • Intel FPGAs / Altera |
1. What happened to Altera?
In 1994, Altera acquired the PLD business of Intel for $50 million.
2. Is Altera owned by Intel?
In June of 2015, chip behemoth Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) announced that it intended to buy Altera, a major supplier of chips known as field-programmable gate arrays, or FPGAs, for $16.7 billion.
3. What is Altera software?
The Altera Quartus II design software provides a complete, multiplatform design environment that easily adapts to your specific design needs. It is a comprehensive environment for system-on-a-programmable-chip (SOPC) design. ... ModelSim software. DSP Builder (requires additional license) Qsys.
4. What is Altera Cyclone?
Altera Cyclone? II 90nm FPGAs are built from the ground up for the low cost and provide a customer-defined feature set for high volume, cost-sensitive applications. ... By minimizing silicon area, Cyclone II devices can support complex digital systems on a single chip at a cost that rivals that of ASICs.
5. When did Intel acquired Altera?
Intel and Altera announced on June 1, 2015, that they had entered into a definitive agreement under which Intel would acquire Altera for $54 per share in an all-cash transaction valued at approximately $16.7 billion. The transaction closed on December 28, 2015.
6. What did Altera Intel do?
The programmable aspect of Altera's chips is the key reason Intel made the purchase -- and it helps bolster Intel's enterprise prospects. Altera makes what are called field-programmable gate array (FPGA) chips, which allow companies to tweak processors in order to better serve their needs.





