
IGBT stands for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, which is an electronic component widely used in power electronics applications such as industrial motor drives, AC converters, and UPS systems. Its working principle involves controlling the conductivity and cutoff of the transistor by applying a control voltage to its gate. IGBT's main advantage lies in its high current-carrying capacity, similar to that of a bipolar transistor, combined with the high input impedance of a MOSFET, making it an efficient power switch that can operate at high frequencies with low switching losses and high-temperature tolerance.
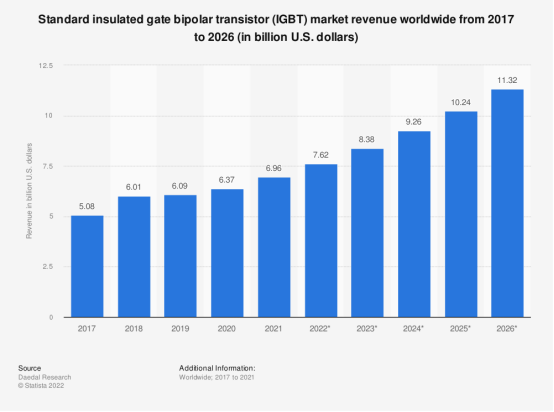
According to Statista data, the global market value of standard IGBT reached 6.96 billion U.S. dollars in 2021, with a projected increase to 7.62 billion U.S. dollars in 2022. By the end of the projected period in 2026, the IGBT market is expected to reach 11.32 billion U.S. dollars.
IGBT's usage in power electronics applications is becoming increasingly widespread, particularly in the fields of new energy and environmental protection. It can be used to control the output current and voltage of solar panels, as well as the motor drive system of electric vehicles.
With the continuous development of new energy and environmental protection, there is a growing demand for high-efficiency and low-loss power electronic devices, and IGBT has great potential for future development. It will be widely used in fields such as smart grids, smart homes, and smart factories to achieve more efficient, safe, and reliable power control and management.




