
In this guide, we will explore the process of enhancing a ZTE router's functionality. By installing a specialized control card, this seemingly modest router can be converted into a compact and efficient mini server. Read on to discover the step-by-step procedure and benefits of this upgrade.
The 847 Control Card:
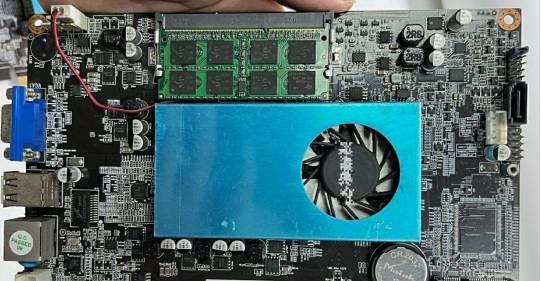

The key component in this upgrade is the 847 control card, often utilized in mining operations. Originally named after the Intel Celeron 847 CPU, these control cards now accommodate various CPU types. In our case, we employ the energy-efficient Intel Core i3-3217U processor, making it a suitable fit for the router's casing.

Modifications:
1. Ventilation Enhancement: To ensure proper cooling, additional ventilation holes are introduced on the control card, blending seamlessly with the router's aesthetics.
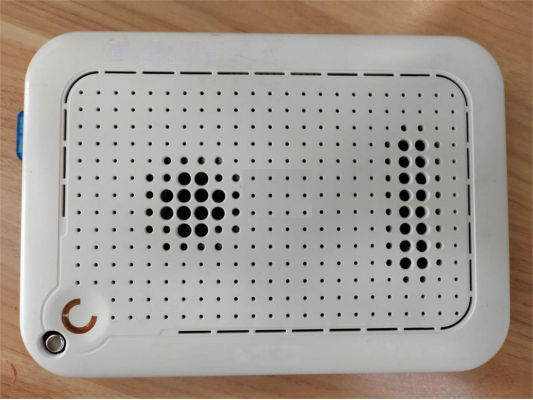

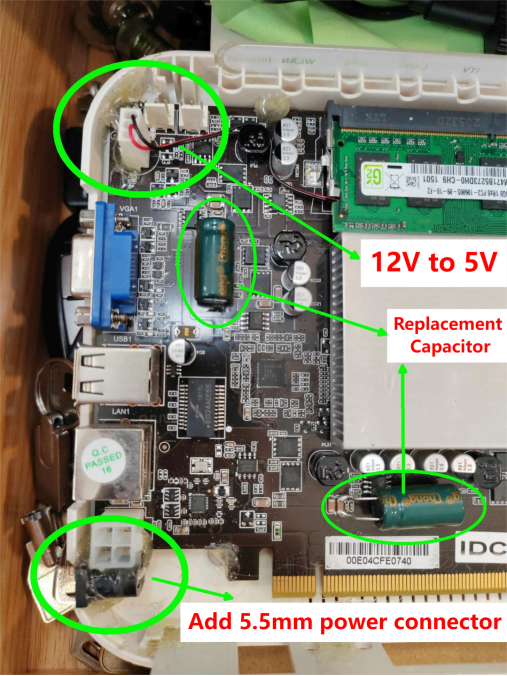
2. Noise Reduction: The original 12V fan is adapted to a 5V power source, significantly reducing operational noise while maintaining the system's temperature under 60 degrees.

3. Power Compatibility: The control card's power supply is addressed by introducing a 5.5mm universal interface adjacent to the original 4-pin connector. Testing reveals stable performance with voltages ranging from 9V to 15V, drawing a modest 2A current.
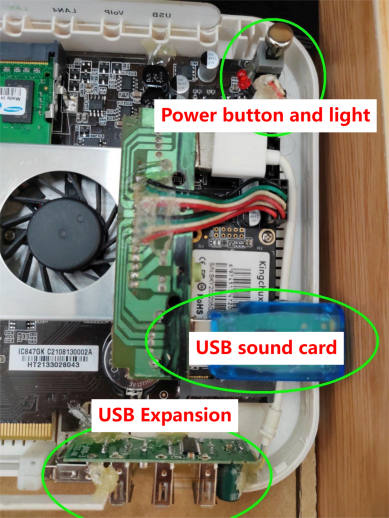
Peripheral Additions:
To make the most of this upgraded router, several peripherals are introduced, including a USB sound card, a USB 4-port hub, and a wireless network card. These additions effectively transform the router into a versatile mini server.
Conclusion:
Upon completion of these modifications, the ZTE router evolves into a capable mini server. While it may not boast top-tier hardware performance, it is more than adequate for everyday web browsing and video consumption. This upgrade transforms an ordinary router into a versatile, cost-effective solution for various computing needs.




