
The air conditioner remote is always getting lost or you just can't seem to find it, and the phone's built-in IR blaster always needs to rescan and reset the connection. So what should you do? In this article, we'll walk you through how to DIY a Xiaomi AC infrared remote that can even link up with Xiao Ai. If you're curious, take a look and see how to make your own IR remote for the AC. That way, you won't have to worry about losing the remote anymore, and you can enjoy true AC freedom in the summer.
So let's follow along and DIY a universal remote.
First is the hardware part. The main MCU is of course the 8266, since it's cheap, supports Wi-Fi, and most 8266 development boards are quite capable now. The rest of the materials are just an infrared receiver and an infrared transmitter.
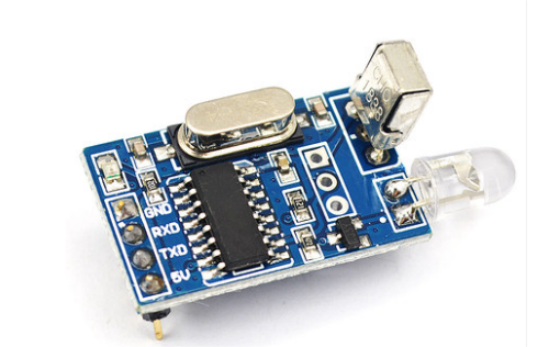
The infrared receiver looks like this:

The infrared transmitter looks like this:

Of course, you can use this type too, but it's a bit more expensive than the one above. And since we're handling all decoding and encoding through Arduino libraries, you don't need one with a built-in chip.
For the software part, you'll need to load two essential libraries. Both are included in the attachment, and you just copy them into the following directory:
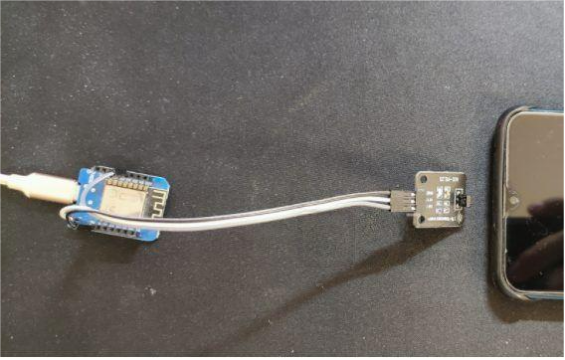
Learning the remote control codes starts with connecting the IR receiver module to the 8266:
VCC → 5V
GND → GND
DATA → D5
After that, open Arduino and go to File -> Examples -> IRremote8266 and find the sample called IRrecvDumpV2, then upload it.
Once it uploads successfully, open the Serial Monitor under the Tools menu. You might see some random noise caused by interference—just ignore it. Grab your AC remote and point it at the IR receiver, like this:
Press the button you want to learn. Here you'll need two buttons: Power On and Power Off. If everything goes smoothly, you'll see something like this in the serial output:

Write down this RawData array, because you'll need it later for playback.
Playing back the learned codes
Once you have the codes from the remote, the next step is to replay them. To make it work with Xiao Ai, you'll also need a little middle-layer platform. Here, you can use Blinker.
Download the Blinker mobile app, hit the plus sign in the top-right to add a device, choose Independent Device, then Network Access, select Alibaba Cloud as the service provider, and note down the key it gives you.
Next, unplug the IR receiver module and replace it with the IR transmitter module. The pin order is the same, so no wiring changes needed:

Open your Arduino code, update the key, Wi-Fi name and password, and paste in the RawData you learned earlier. Then upload.

If you're interested in the code, you can check out the official dev manual here: https://www.diandeng.tech/doc/xiaoai. If everything works, your device should already be online.
Adding buttons and linking to Mi Home
In the Blinker app, tap your device, hit the little pencil icon in the top-right, and add two buttons. Name them btn-pwron and btn-pwroff, then save.
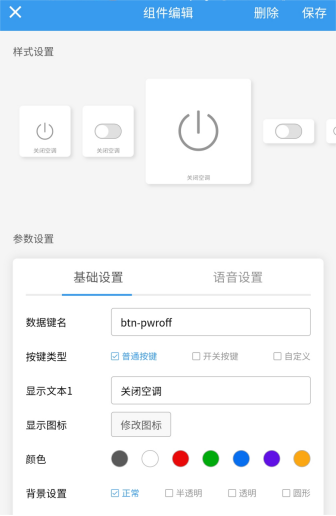
After saving, try pressing the buttons to see if the AC responds normally.
Next, go to Mi Home → Profile → Other Platform Devices → Link Blinker account, then sync. If it succeeds, you should see your device:
Then try calling Xiao Ai and test whether the remote commands work normally.
And that's it—you're done. Now you've got your very own universal remote.
Code: https://github.com/bznsix/8266IrRemote
Or just download it directly from this attachment.




