
Discover the delight of crafting your own personalized nightlight using readily available components such as spare batteries and LED lights.
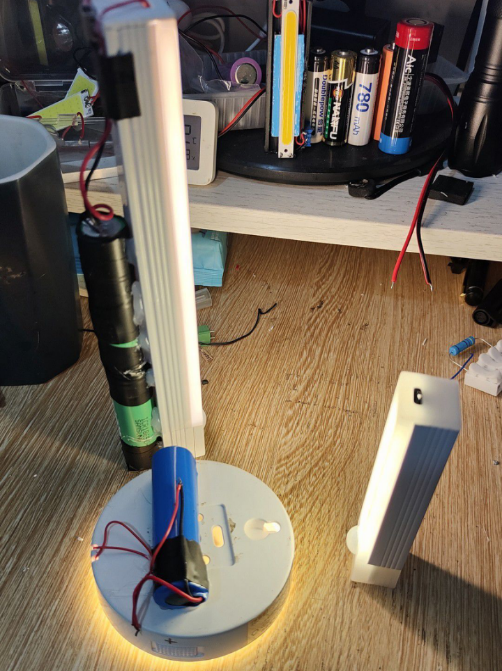
The primary components of this motion-sensor nightlight project include the HC-SR501 module, a light-dependent resistor, the S8050 transistor, LED lights, a lithium battery, a DC boost module, and a charging module.

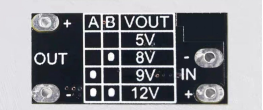
The lithium battery in use boasts a rated voltage of 3.7V. To ensure a consistent 5V output for the HC-SR501 module, you need to incorporate a compact boost module.
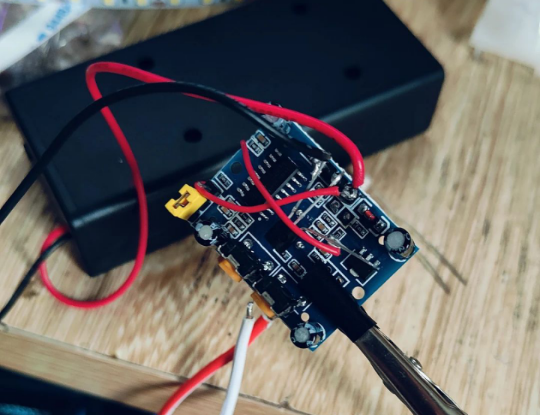
For battery management and protection, we employ the widely-used TP4056 charging and discharging module. This module safeguards against overcharging and over-discharging, ensuring the longevity of your nightlight.
Follow the comprehensive wiring diagram, skillfully solder the connections for each module, create necessary openings, and secure them firmly with hot glue.
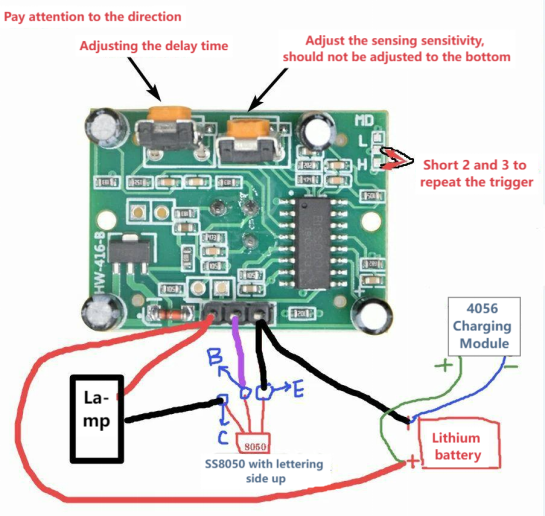
In the event that you lack a hole punch tool, a soldering iron can serve as a suitable alternative.

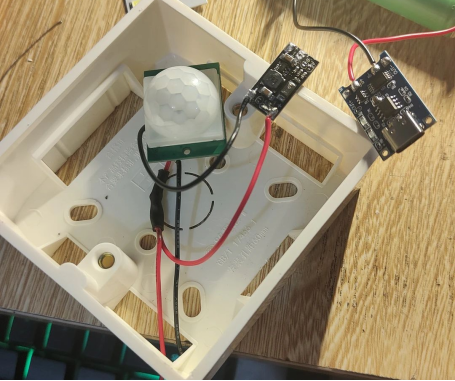
To house your nightlight, consider utilizing an 86 surface-mounted junction box. Make the necessary adjustments to accommodate two 18650 batteries, securing them on the top portion while reserving space at the bottom for the charging module.
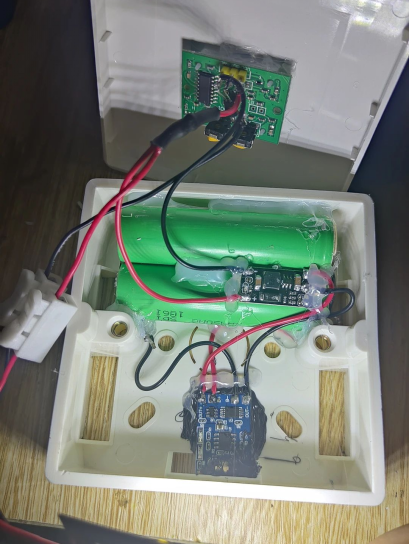

For the output terminal, utilize connectors for added versatility. This allows you to easily connect various lights in different locations, such as 5V LED strips. Alternatively, introduce a resistor to regulate voltage for the LED lights. For those seeking even greater flexibility, consider implementing an adjustable boost module to elevate the output to 12V for mainstream light strips. Adjust brightness levels either by reducing voltage or incorporating resistors in series.
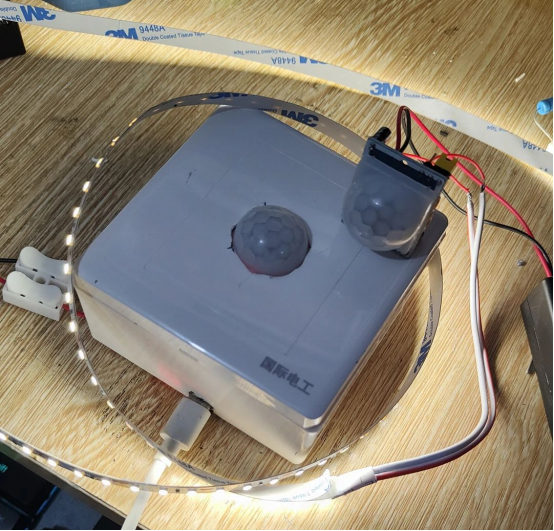


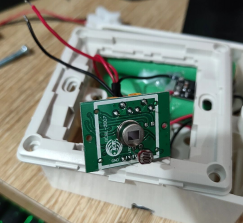
While this project has demonstrated practicality, it's worth noting that the sensor may activate in low-light conditions. If you find it activating too early with the 5516 sensor, consider upgrading to the 5539 sensor. For further fine-tuning, you have the liberty to customize the sensitivity to meet your specific preferences.




