
In today's digital age, the electronic components industry is thriving, with digital isolators being a key focal point. This article delves into the definition, characteristics, advantages, and different types of digital isolators.
Catalog
I. What are Digital Isolators?
IV. How Does a Digital Isolator Work?
V. How Do Capacitive Digital Isolators Work?
VI. How Does Edge-Based Isolation Work?
VII. How Does On Off Keying (OOK) Isolation Work?
I. What are Digital Isolators?
Galvanic isolation is utilized to prevent DC and unwanted AC currents between two parts of a system while allowing signal and power transfer between them.
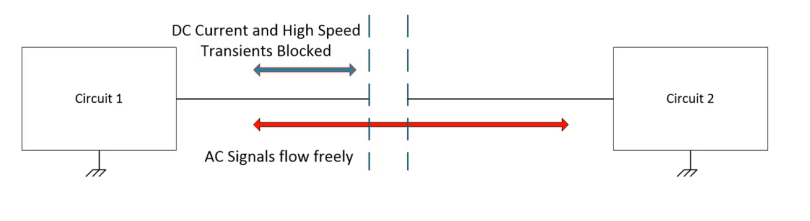
Digital isolators are integrated devices used to isolate digital signals and facilitate digital communication across an isolation barrier between microprocessors and data converters. Typically, they come into play after the ADC in a system, bridging microprocessors and FPGAs operating at different supply levels or interfacing communication boards sharing backplanes.
II. Features and Advantages
· High-Speed Transmission: Digital isolators enable high-speed data transfer, suitable for applications requiring rapid responses.
· Strong Interference Resistance: They effectively fend off external interference, ensuring signal stability and reliability.
· Excellent Isolation Performance: Digital isolators efficiently isolate signals between different circuits, averting potential circuit shorts and damages.
· High-Temperature and High-Voltage Resistance: Digital isolators typically boast excellent resistance to high temperatures and voltages, suitable for various demanding operating environments.
III. Types
Digital isolators come in several types based on their working principles and structures, including:
· Optocoupler Digital Isolators: Utilizing optoelectronic coupling principles, these isolators commonly employ a combination of LEDs and photodiodes. Such as ADuM1200.
· Magnetic Digital Isolators: Using magnetic field coupling principles, these isolators typically comprise coils and transformer structures. Such as ISO7740.
· Capacitive Digital Isolators: These isolators transmit signals through the dielectric between two capacitors—one at the input and the other at the output. Such as Si823Hx.
IV. How Does a Digital Isolator Work?
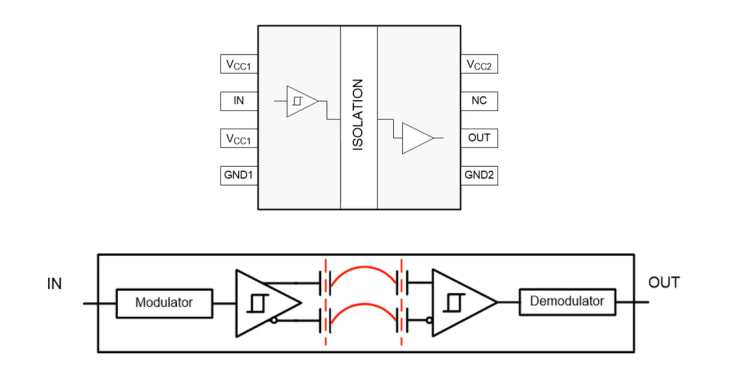
A digital isolator typically consists of two isolated supplies (VCC1 and VCC2), two grounds (GND1 and GND2), and input and output pins on either side. The input signal is modulated through a transmit IC, passed through a high-voltage capacitive barrier, and received by the receiving side IC.
V. How Do Capacitive Digital Isolators Work?
Capacitive digital isolators utilize the dielectric between two capacitors for signal transmission. When the input signal changes, the electric field between the capacitors also changes, generating a corresponding signal at the output.
VI. How Does Edge-Based Isolation Work?
Edge-based isolation efficiently isolates signals by utilizing the rising and falling edges of signals. Additional delay time is added at the signal edges to ensure effective isolation between input and output.
VII. How Does On Off Keying (OOK) Isolation Work?
OOK isolation, based on digital modulation, transmits information by toggling the signal's state. High voltage signifies logic 1, while low voltage signifies logic 0, enabling efficient digital signal isolation and transmission.
VIII. Conclusion
Digital isolators play a pivotal role in the electronic components industry, offering fast and reliable signal transmission while effectively combating external interference to enhance system stability and reliability.




