
If you're interested in the firmware of the ink screen temperature and humidity sensor, take a look at this article.
In this DIY guide, we will discuss the temperature and humidity sensor from Haier, model MHO-C401.
Haier's own app allows you to view the temperature and humidity on your phone, but it doesn't seem to serve much other purpose since it lacks the functionality to display historical data. This sensor model is identical to a similar one from Xiaomi, but it cannot connect directly to the Mi Home app—it will fail. Considering Xiaomi's custom firmware culture, you might want to check out the project at https://github.com/pvvx/ATC_MiThermometer for reference.
Xiaomi's app communicates with the sensor using the MiBeacon protocol. The broadcast identifier must include a "service data" field in the broadcast that contains Xiaomi's service, and the "manufacturer-specific data" in the scan response must include Xiaomi's company ID. When using nRF Connect, you'll see the Xiaomi service, but you might not see the company ID. Additionally, Xiaomi devices also have a device key, which is why you may encounter a security authentication failure with the error code -27.
At the same time, the ink screen may stop refreshing. If there's a slight difference in screen color, it's likely because a different screen model is being used.
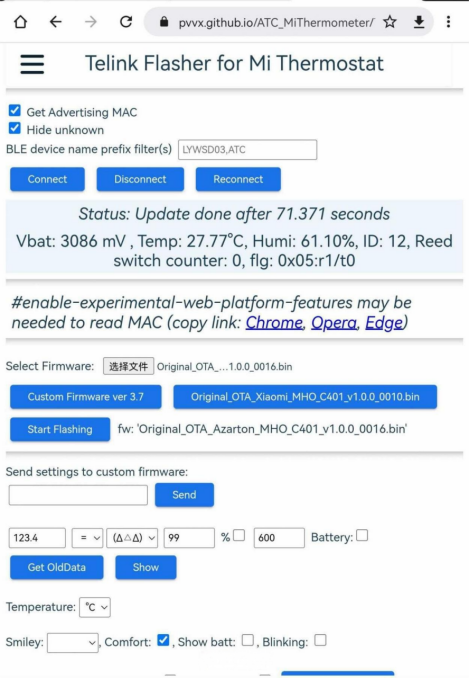
Be sure to check the firmware file called "Original_OTA_Azarton_MHO_C401_v1.0.0_0016.bin" on the firmware introduction page. This firmware isn't available in the flashing and configuration sections, so you'll need to manually download it to your local device and then upload it through the flashing page to use it.

End.




