
In the previous DIY article, DIY ESP8266 Xiaomi AC Infrared Remote Guide, we talked about making a universal infrared remote. This time, we'll continue with how to DIY an infrared remote. But in this DIY guide, we're going to modify the AI-Win Tech WiFi infrared remote from AI-Win Tech. If you're interested, keep reading.
The appearance is shown in the picture below—it's a small box and looks quite neat.
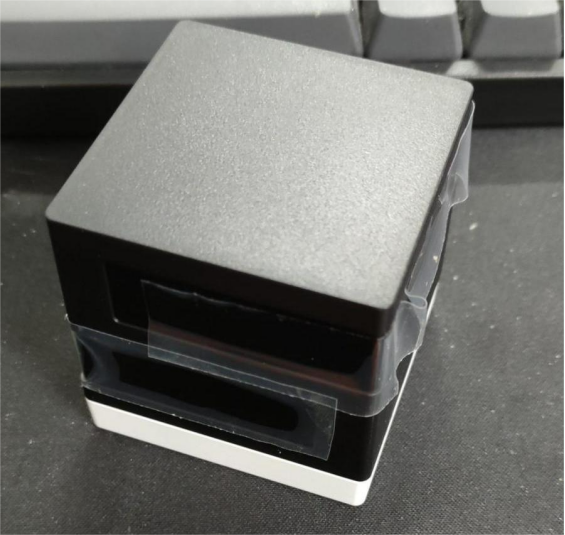

The bottom looks like this; it has rubber feet and screws underneath.

Usually, this kind of MCU is basically an 8266. The internal circuit structure looks like this:
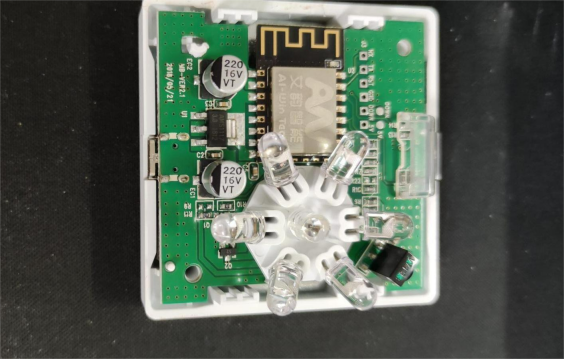
The back looks like this, and you can see it's just an ESP8266.
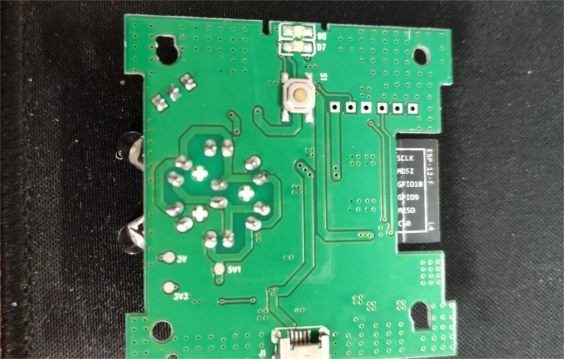
You'll need to prepare some infrared diodes.
The pin diagram looks something like this. The transistor is designed in a clever way. Normally, after modulating and transmitting an infrared waveform once, the IO pin stays in a low state. At this point, the transistor that amplifies the infrared signal is turned on, so the infrared diode, 5V, and ground are all connected. If the quality is good, it won't get damaged or overheat when you start the program.
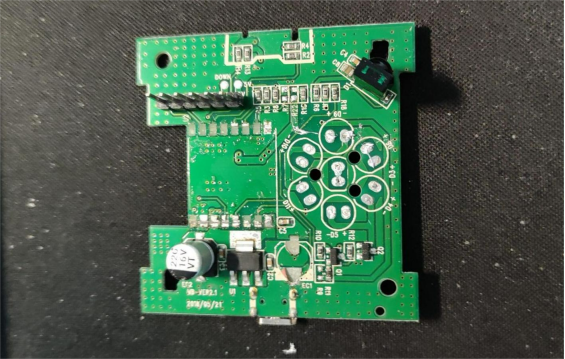
The expected features are:
1. Supports Smart Config for network setup
2. It can learn infrared remote codes
3. Using the WiFi manage library may conflict with EEPROM usage
4. Press a button to start learning, and ideally, an LED should indicate a successful learning
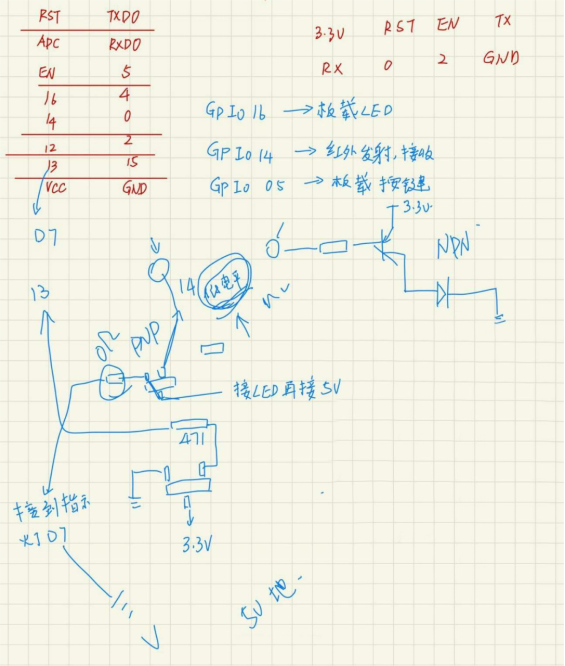
For flashing the firmware, you just need to solder a row of pins on the right side, and everything will be accessible. The “DOWN” pin is connected to IO0, which should be connected to ground during flashing.
Finally, here's the code: https://github.com/bznsix/8266IrRemote
For the build tutorial, you can refer to the previous DIY article.
This remote has a button on it, so you could also experiment with making a transmitter-integrated version.




