
In the electronics industry, ordinary diodes are essential components that cannot be omitted in anything from basic circuits to complex systems, and silicon diodes and germanium diodes are two of the most common PN junction diodes, classified according to their semiconductor materials. This article will systematically explain the core differences between silicon diodes and germanium diodes and will focus on a practical resistance measurement method using a multimeter to distinguish them.
Catalog
II. What is a germanium diode?
I. What is a silicon diode?
A silicon diode is an electronic device that uses silicon as the PN junction semiconductor substrate and forms P-type and N-type regions through doping. Silicon has a relatively wide bandgap of about 1.12 electron volts, which makes silicon diodes exhibit a higher forward voltage drop during operation, usually around 0.7 volts. Silicon diodes can withstand a relatively high temperature range, have good thermal stability, and have low reverse leakage current, which makes them widely used in power rectification, voltage regulation circuits, switching circuits, and general electronic systems. Silicon is abundant and low in cost, which is an important reason why silicon diodes dominate industrial production.
II. What is a germanium diode?
A germanium diode is a PN junction semiconductor device made from germanium material. Germanium belongs to group IV of the periodic table and, like silicon, has semiconductor properties, but its bandgap is smaller at about 0.67 electron volts, which results in a lower forward voltage drop, usually around 0.3 volts. This lower forward voltage drop gives germanium diodes advantages in low-voltage signal detection, audio circuits, and some radio frequency reception circuits. Germanium diodes have poorer thermal stability and higher reverse leakage current compared to silicon diodes, so their performance is more affected in high-temperature environments, and they are therefore less commonly used in most modern high-temperature or high-power applications.
III. Differences
The differences between silicon diodes and germanium diodes come from the distinct physical and chemical properties of their core materials, and these differences are reflected in several key parameters.
1. Forward voltage drop differs. This is the most direct way to distinguish them, with silicon diodes around 0.6 to 0.7 volts and germanium diodes only about 0.1 to 0.3 volts. This difference directly affects their conduction ability in low-voltage circuits.
2. Reverse characteristics are distinct. Silicon diodes have extremely small reverse saturation current, usually in the nanoampere range, and very high reverse resistance, while germanium diodes have reverse leakage current hundreds to thousands of times larger, typically in the microampere range, and relatively lower reverse resistance.
3. Temperature tolerance and thermal stability vary greatly. Silicon diodes can operate at higher junction temperatures and remain thermally stable, whereas germanium diodes are temperature sensitive and their performance degrades sharply at high temperatures.
4. Voltage tolerance differs. Silicon material allows for diodes with reverse voltage ratings of hundreds or even thousands of volts, while germanium diodes usually have maximum reverse voltages of only tens of volts.
5. Manufacturing cost and application areas differ. Silicon is abundant and its manufacturing process is mature, which dominates most applications, while germanium diodes are mainly used in specific areas such as signal detection requiring low-voltage conduction or certain retro audio circuits due to cost and performance limitations.
IV. How to distinguish?
When the diode model is unclear, using a pointer multimeter with the resistance measurement method is one of the classic and effective ways to distinguish silicon diodes from germanium diodes. This method relies on the significant difference in forward resistance between the two types to make a judgment.
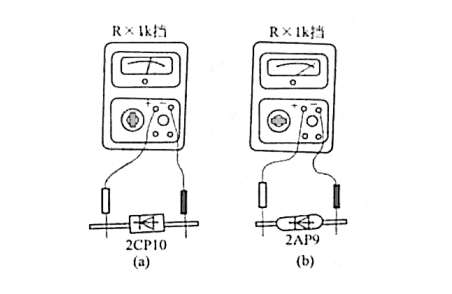
Silicon diodes have a higher forward conduction voltage than germanium diodes and a smaller reverse saturation current in reverse operation. This difference is reflected in the DC resistance, with both the forward and reverse resistance values of silicon diodes being higher than those of germanium diodes. Therefore, by testing the forward resistance value, you can determine whether the diode being tested is silicon or germanium.
The test method is to set the multimeter range switch to R×100 or R×1k, measure the diode's forward resistance, and judge based on the pointer deflection on the meter dial. If the pointer points to the middle-right position of the scale, around 4 to 8 kΩ, the diode is a silicon diode, as shown in figure (a). If the pointer deflects close to the zero position, the diode is a germanium diode, as shown in figure (b).
V. Conclusion
Understanding the essential differences between silicon diodes and germanium diodes is not only part of mastering semiconductor device characteristics for electronics engineers, but it is also fundamental knowledge for actual circuit design, debugging, and maintenance. Silicon diodes are widely used in modern electronic systems due to their high thermal stability, low reverse leakage current, and high power handling capabilities, while germanium diodes still have irreplaceable value in specific applications because of their low forward voltage characteristics.




