
In the electronic components industry, decoders are powerful logic integrated circuits (ICs) widely employed in digital systems. This article will cover aspects of decoders including their definition, characteristics, advantages, and application domains.
I. What are Decoders in Logic ICs?
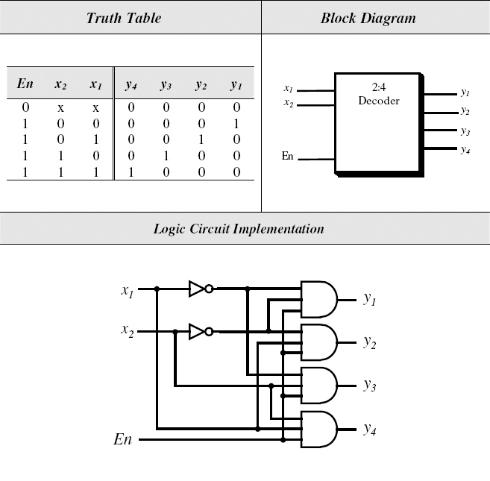
A decoders is a multiple-input, multiple-output logic circuit that converts coded inputs into coded outputs, where the input and output codes are different. The input code generally has fewer bits than the output code, and there is one-to-one mapping from input code words into output code words.
II. Characteristics & Advantages
· Versatility: Decoders can execute various logical functions such as decoding, data selection, and signal routing.
· Flexibility: Input and output configurations of decoders can be flexibly adjusted to meet diverse design requirements.
· High Performance: Modern decoders boast excellent performance metrics including high speed and low power consumption, suitable for a wide array of digital systems.
· Reliability: Leveraging integrated circuit technology, decoders offer stable and reliable performance, capable of sustained operation over extended periods.
III. Applications
Decoders find extensive applications in the electronics domain, including but not limited to:
· Digital Displays: Utilized to translate input signals into control signals for devices like numeric displays and LCD screens. For instance, the 74HC238 can translate binary signals into corresponding drive signals for numeric displays.
· Memory Address Selection: Employed to identify address signals within memory, facilitating selection and access of memory units. For example, the commonly used 3-to-8 decoder 74LS138 converts input address signals into corresponding memory module selection signals, enabling unit positioning and access.
· Data Selection: Used to select specific data outputs from multiple input data sources, often applied in data switching and routing control. For instance, a 16-channel analog multiplexer like the CD74HC4067 can route one of its channels to the output based on control signals, facilitating data selection and switching.
IV. Packaging
Decoders are typically supplied in chip form, featuring various packaging types and specifications to suit different application needs. Common packaging types include Dual Inline Package (DIP) and Small Outline Package (SOP).
V. Conclusion
Decoders stand as crucial components in the electronic components industry, providing indispensable support for the connection and control of digital systems. Their flexibility, high performance, and reliability ensure significant contributions across diverse application scenarios.




