
Photoresistors are an essential part of the modern electronics industry. They are highly regarded for their sensitivity to light and their wide range of applications. In this article, we will delve into the definition, working principle, characteristics, advantages, and applications of photoresistors.
Catalog
III. Characteristics and Advantages
I. What are Photoresistors?
A photoresistor, also known as a photocell, light-dependent resistor (LDR), or photoconductive cell, is a passive electronic component whose resistance decreases as the luminosity (light) on its sensitive surface increases. In other words, it demonstrates photoconductivity. A photoresistor can be used in light-sensitive detector circuits, as well as in light-activated and dark-activated switching circuits, functioning as a semiconductor resistor.
II. Working Principle
The working principle of a photoresistor is based on photoconductivity, which is the sensitivity of semiconductor materials to light. When light strikes the photoresistor, electrons in a stable state within the resistor become energized and transform into free electrons. The stronger the light, the more free electrons are generated, resulting in a lower resistance. In darkness, a photoresistor can have resistance as high as several megaohms (MΩ), while in the light, it can drop to just a few hundred ohms. When the frequency of incident light on a photoresistor exceeds a certain threshold, photons absorbed by the semiconductor provide bound electrons with enough energy to jump into the conduction band. The resulting free electrons (and hole pairs) conduct electricity, lowering resistance.
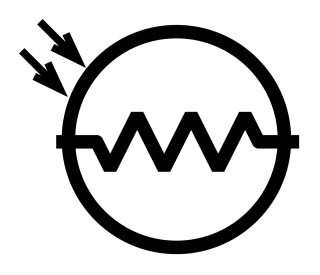
△ The symbol for a photoresistor
III. Characteristics and Advantages
· High Sensitivity: Photoresistors are highly sensitive to changes in light intensity, allowing for a rapid response to variations in illumination.
· Low Cost: Photoresistors are relatively inexpensive to manufacture, making them widely used in the electronics industry.
· Ease of Use: Photoresistors are easy to wire and operate, making them simple to integrate into various electronic circuits.
· Durability: Photoresistors have a long lifespan and stable performance, enabling them to operate reliably even in harsh environments.
IV. Applications
Photoresistors have a broad range of applications, including but not limited to:
· Lighting Control: Used to automatically adjust lighting brightness or turn on lights when ambient light levels are low.
· Cameras and Camcorders: Employed to automatically regulate exposure time and aperture for improved image quality.
· Fire Alarm Systems: Used to quickly detect and alert of fire through changes in light intensity from flames.
· Smart Home: Utilized to monitor ambient light levels and automatically control curtains, lights, and other devices.
V. Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the application prospects for photoresistors in the electronics industry are vast. They will play an increasingly significant role in smart devices, the Internet of Things, autonomous vehicles, and other areas. In the future, we may see more sensitive and efficient photoresistors designed to meet the needs of high-end applications.




